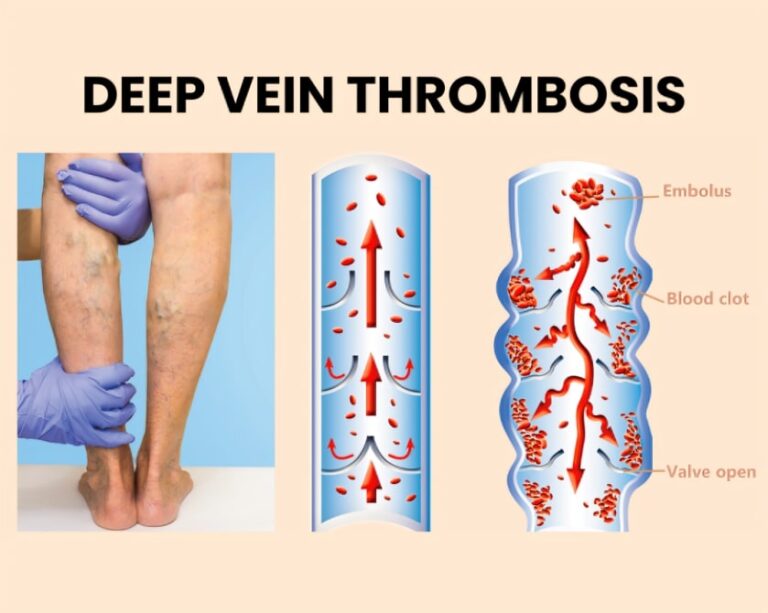
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
DVT, or Deep venous Thrombosis, is a widespread occurrence in patients after surgery or even in patients with a long history of immobilization. Untreated, deep vein thrombosis can give rise to life-threatening complications such as pulmonary embolism and, therefore, requires urgent attention. Get the best DVT treatment from top-class surgeons in the country with the help of Medintu.
Fill out form to enquire now
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis?
Deep vein thrombosis is a complication in which there is the formation and extension of a clot or thrombus within the blood vessel or vein. It is more commonly seen in the lower limbs and the deeper veins of the leg. Prolonged immobilization and mutations in anti-clotting factors can lead to clotting and cause this condition in many people.
Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis:
Simple lifestyle changes, as well as medications, can help prevent DVT in high-risk patients.
- Living an active lifestyle improves blood circulation in the body.
- Losing weight in cases of obesity or maintaining a healthy weight.
- Keep hydration levels adequate by drinking lots of water.
- Compression stocking during bed rest or a long period of immobilization
- Stop smoking to reduce the coagulability of the blood.
- Keep chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension in check.
- Take anticoagulation medication as prescribed by the doctor, especially if you have a condition that increases your chances of developing DVT.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Causes:
The causes of deep vein thrombosis are as follows:
- Long periods of immobility
- Hormonal excess, as in OCP and hormone replacement therapy in women
- Pregnancy and the postpartum period
- Obesity as it interferes with blood circulation
- Smoking as it increases the coagulability of blood
- Varicose veins and other conditions cause poor blood flow in the lower limbs
- Hereditary diseases such as factor V Leiden or prothrombin gene defect.
- Cancer and cancer treatment
- Recent major surgery and immobilization.
What is the procedure for DVT treatment?
Once DVT is diagnosed, the doctor will advise on the treatment best suited for you and start it immediately after some blood tests for clotting and bleeding. In surgery or radiological intervention cases, a pre-anesthesia checkup is also done. Once the checkup is over and the patient is declared fit for surgery, the time is decided, and the patient is admitted to be operated on. The night before the operation, IV fluids are stopped, and directions for nil per oral are given. Part preparation is done on the day of surgery or radiological intervention for DVT, and the patient is shifted to OT on call. Once the procedure is done, the patient is moved to an observation room, where they are observed for 3–4 hours before being shifted to the ward. Once the patient is on the road to recovery, they are discharged.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Treatment:
DVT can be treated with the help of medical therapy, surgery, or interventional radiology practices.
Medical therapy:
DVT can be treated with anticoagulants, such as Heparin, Warfarin, or direct oral anticoagulants. These help break the clot and prevent it from extending through the vessel to become more prominent.
Surgery for DVT:
In extensive clots or suitable patients, a surgical procedure called thrombectomy removes the chunk before it breaks off and causes complications.
Interventional radiology:
The placement of a green filter in the large veins is done with the help of catheters under radiological guidance. The method is suitable for patients with a genetic tendency to form clots or patients not eligible for the above treatment.
Supportive management for DVT:
Interventional radiology is a simple and non-invasive measure to treat and prevent DVT, such as:
1.Compression stockings are used, which help provide a gradient of pressure over the leg and thus prevent blood stasis in leg veins.
2.Leg elevation can reduce swelling and improve blood circulation.
Complications of DVT:
Deep vein thrombosis, if not treated in time, can lead to the following complications:
- Pulmonary embolism can cause clots to reach the lung and cause pulmonary hemorrhage and ischemia by blocking pulmonary arteries.
- Post-thrombotic syndrome, in which there is chronic pain and swelling in the skin of the leg affected by DVT.
- There can be a recurrence of DVT.
- Chronic venous insufficiency, in which blood can pool in the legs due to damage to the valves.
- In rare occurrences, the clotting and bleeding mechanisms can be dysfunctional, leading to DIC or disseminated intravascular coagulation.
- Gangrene of the limb.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Risk Factors:
Deep vein thrombosis increases the chances of clot formation in people with certain risk factors. Some of them are as follows:
- Recent major surgery, such as abdominal or arthroplasty.
- Prolonged immobilization, such as a coma
- Certain genetic conditions cause S and C deficiency.
- Cancer patients, patients with heart disease, and those with a history of DVT have an increased tendency.
- Use of birth control pills or hormone replacement therapy.
- Older age
- Obesity
- Smoking
- varicose veins and peripheral vascular diseases.
Deep Vein Thrombosis Symptoms:
Deep Vein Thrombosis Signs and Symptoms are as follows:
1.Pain during walking.
2.Cramping pain in the calf.
3.Tenderness on pressing in the calf.
4.Pain increased when stretching the leg.
5.Changes in the skin over the affected leg.
Why Choose Medintu?
Medintu is one of the most advanced online medical platforms, aiming to bring affordable medical care to your doorstep. We emphasize quality and are associated with the most trained professionals in their expertise. Our services are available as home-based care in Hyderabad, Bangalore, Ahmedabad, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram, Kolkata, Pune, and Mumbai.
Contact our esteemed general medicine practitioners and cardiologists to manage DVT with a head-on approach. Our doctors are equipped with the latest knowledge on DVT treatment and use state-of-the-art technology to treat the condition. Get the best medical and surgical treatment for DVT with Medintu.
FAQs
What is the treatment duration for DVT?
Immediate management with surgery and interventional radiotherapy will last as long as the procedure, 45 minutes to 1 hour. The medical management of DVT with anticoagulation can continue lifelong, with the drugs being changed as needed.
Can DVT occur after treatment?
Yes. Having a DVT once can lead to increased chances of having it again, especially in the presence of known risk factors. Therefore, it is vital to continue lifestyle modifications as well as medications for preventing DVT lifelong.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Pulmonary embolism is the lodging of a small clot from a DVT, and it’s usually caused by deposition in the pulmonary arteries, causing a blockage and, thus, symptoms of breathlessness and blood in the sputum.
How common is DVT?
DVT is a prevalent vascular accident in adults, with the incidence increasing with age.
Can there be DVT in healthy young adults?
Yes, a family history of DVT, major risk factors for DVT, and poor habits like smoking can increase the risk of DVT in young adults as well.
Is DVT family history a sign of DVT being a hereditary condition?
Disorders of some proteins that cause clotting can lead to DVT, such as factor V Leiden mutation and mutation of prothrombin gene.
What is the most common site of DVT?
The most common site for DVT is the deep leg vein called femoral vein, and calf veins, called the popliteal vein. Sometimes, it can even occur in the veins of the upper limb.
What is the cost of treatment for DVT?
The cost of deep vein thrombosis treatment can be anywhere from 80,000 to 1,50,000 rupees, depending on the patient’s condition, the severity of the DVT, the size of the thrombus, the technique used, the doctor, and the hospital.
How is deep-vein thrombosis diagnosed?
A deep vein thrombosis is initially a clinical diagnosis through clinical history, signs, and symptoms that indicate the high probability of a thrombus in a deep vein. The diagnosis is confirmed with the help of radiological investigations.