Fill out form to enquire now
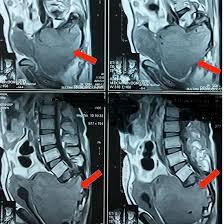
MRI Sacrum Scan
Medintu has collaborated with the best pathology laboratories that are NABL and NABH certified and follow ISO safety guidelines to provide the best MRI For Sacrum Scan at an affordable price for needy individuals. An MRI for Sacrum Scan is a non-invasive diagnostic imaging procedure that uses powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the sacrum and surrounding structures, such as the pelvic bones, nerves, muscles, and soft tissues. The sacrum is the triangular-shaped bone at the base of the spine, forming the back portion of the pelvis. It plays a critical role in supporting the weight of the upper body and connecting the spine to the lower limbs. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) is a safe and effective tool used by healthcare professionals to evaluate the sacral region for conditions that may affect mobility, cause pain, or interfere with daily activities. Unlike traditional X-rays, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a preferred choice for diagnosing a variety of spinal and pelvic disorders. An MRI of the sacrum is typically recommended when a patient presents with unexplained pain, numbness, or weakness in the lower back, hips, or legs, or when other imaging techniques (such as X-rays) are insufficient to provide a clear diagnosis. Whether assessing degenerative conditions, spinal fractures, tumors, or nerve compression, MRI provides a high level of detail to help doctors develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
To schedule an appointment for a MRI For Sacrum Scan, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is a Sacrum and Why is it Important?
The sacrum is a large, triangular-shaped bone located at the base of the spine, just above the coccyx (tailbone). It is a key part of the pelvic region and plays an essential role in providing support and stability to the body. Here’s why the sacrum is so important:
Anatomy of the Sacrum
1.Position and Structure: The sacrum is located between the two hip bones (iliac bones), forming the back portion of the pelvis. It consists of five fused vertebrae (S1-S5) that are joined together, creating a solid, triangular structure.
2.Joints: The sacrum connects to the lumbar spine at the top and to the coccyx (tailbone) at the bottom. It also forms sacroiliac joints with the iliac bones of the pelvis on either side. These joints help absorb shock and transfer weight from the upper body to the lower extremities during movement.
Why is the Sacrum Important?
1.Supports Body Weight:
The sacrum plays a central role in transferring weight from the upper body to the legs and hips. It acts as a foundation that supports the spinal column, ensuring stability and balance during standing, walking, and other movements.
2.Spinal Column Connection:
The sacrum is part of the spinal column, connecting the lumbar spine (lower back) to the pelvic bones. This connection helps maintain postural alignment and supports the natural curves of the spine.
3.Provides Structure to the Pelvic Region:
The sacrum is crucial for the shape and structure of the pelvic cavity. It forms a solid base for the pelvic organs, including the bladder, rectum, uterus, and ovaries in females, and the prostate and rectum in males.
4.Protects Nerves:
The sacrum encases and protects important nerve pathways that control lower body functions. The sacral nerves that exit from the sacral vertebrae are part of the sciatic nerve, which controls movement and sensation in the legs and feet.
5.Supports Posture and Movement:
The sacrum helps distribute forces that occur during physical activities such as walking, running, or lifting. It also allows for the flexibility and movement of the pelvis, especially during childbirth (in females) and various leg motions.
6.Important for Pelvic Floor Function:
The pelvic floor muscles, which support the bladder, uterus, and rectum, attach to the sacrum. The alignment and integrity of the sacrum are vital for proper pelvic floor function, influencing urinary, bowel, and sexual health.
Why is MRI Used for Sacrum Scan?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan of the sacrum is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides detailed, high-resolution images of the sacrum and surrounding structures. Here’s why MRI is commonly used for sacrum scans:
- Non-invasive and Radiation-free Imaging
Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer and non-invasive alternative, especially for patients who may need multiple imaging studies over time. MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images, reducing the risks associated with radiation exposure.
- Detailed Visualization of Soft Tissues and Bones
MRI provides exceptional soft tissue contrast, allowing doctors to clearly visualize not only the bones of the sacrum but also the surrounding nerves, muscles, ligaments, and intervertebral discs. This level of detail is crucial for assessing conditions like sciatica, degenerative disc disease, or muscle injuries in the pelvic and sacral area.
- Identifying Spinal Disorders
MRI is particularly effective in diagnosing degenerative spine conditions like spondylosis, spondylolisthesis, or herniated discs that may affect the sacral region of the spine. It can also detect sacroiliitis (inflammation of the sacroiliac joints) or spondylitis (inflammation of the vertebrae), which may cause pain or discomfort in the lower back and pelvis.
- Detecting Fractures and Trauma
Fractures in the sacrum, often caused by trauma, accidents, or falls, are clearly visible on MRI. MRI is highly sensitive to bone abnormalities and can detect hairline fractures or stress fractures that may not be visible on X-rays.
- Diagnosing Tumors and Infections
MRI is invaluable in detecting abnormal growths, such as benign or malignant tumors, in the sacral region. It is also used to identify infections (such as osteomyelitis or abscesses) in the bones, joints, or soft tissues around the sacrum.
How MRI for Sacrum Scan Works?
An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan for the sacrum uses powerful magnets, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed, high-resolution images of the sacral region and surrounding structures. Here’s how it works:
- Magnetic Field Generation
The MRI machine uses a strong magnetic field to align the hydrogen atoms found in the body’s water molecules. Since the body is made up largely of water, especially in tissues like muscles, organs, and nerves, these hydrogen atoms play a key role in producing clear images.
- Radio Waves to Excite Hydrogen Atoms
Once the hydrogen atoms are aligned, the MRI machine sends radiofrequency pulses to the body. These pulses temporarily “excite” the hydrogen atoms, causing them to emit signals as they return to their original alignment. These signals are what the MRI machine measures.
- Signal Detection and Image Creation
The MRI machine detects the signals emitted by the hydrogen atoms as they return to their original position. Different tissues in the sacrum (such as bones, muscles, nerves, and soft tissues) emit different signals, allowing the MRI to create highly detailed images of the area.
The signals are processed by a computer to create cross-sectional images (also called slices) of the sacrum and surrounding areas. These images can be viewed as 2D or 3D representations on a monitor, allowing doctors to see the region from various angles.
- Detailed Imaging of Soft Tissues and Bones
MRI is particularly effective in imaging both hard tissues (like bones) and soft tissues (like muscles, ligaments, nerves, and discs). This makes it ideal for assessing the sacrum, a complex area that includes the sacral vertebrae, sacroiliac joints, nerves, and surrounding muscles.
The high resolution of MRI allows for the detection of subtle issues such as sacroiliac joint inflammation, spinal cord abnormalities, nerve compression, or muscle damage in the sacral region.
Conditions Diagnosed with MRI for Sacrum Scan
MRI for the sacrum is an essential diagnostic tool that can identify a wide range of conditions affecting the sacral region, lower spine, and pelvis. Its high-resolution imaging ability allows doctors to assess both hard and soft tissues, making it particularly useful for diagnosing complex issues that may not be visible on other imaging modalities like X-rays or CT scans. Here are some of the key conditions that can be diagnosed with an MRI for sacrum scan:
- Degenerative Disc Disease
Description: Degeneration of the intervertebral discs between the sacral vertebrae can cause pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility.
How MRI Helps: MRI can reveal disc bulging, herniations, or loss of disc height in the sacral area, indicating wear and tear on the spine.
- Sacroiliitis
Description: Inflammation of the sacroiliac (SI) joints, where the sacrum meets the iliac bones of the pelvis, often causing lower back and pelvic pain.
How MRI Helps: MRI can detect swelling, fluid accumulation, and bone erosion in the SI joints, providing clear evidence of inflammation or infection.
- Spinal Fractures or Trauma
Description: Fractures of the sacrum can occur due to trauma, such as a fall, car accident, or osteoporosis.
How MRI Helps: MRI is excellent for detecting fractures, hairline fractures, and soft tissue injuries around the sacrum that may not be visible on X-rays.
- Spondylolysis and Spondylolisthesis
Description: Spondylolysis is a stress fracture in the vertebrae, and spondylolisthesis occurs when one vertebra slips forward over the one below it. These conditions can affect the lumbar and sacral vertebrae.
How MRI Helps: MRI can visualize vertebral misalignment, fractures, and any associated damage to the nerves or intervertebral discs.
- Tumors and Cancer
Description: Benign or malignant tumors can develop in the bones, soft tissues, or nerves of the sacral region, including sacral tumors, spinal tumors, or metastases from cancers elsewhere in the body.
How MRI Helps: MRI provides detailed imaging of soft tissues, making it effective for identifying tumors, cysts, or abnormal growths in the sacrum and surrounding structures.
When is an MRI for Sacrum Scan Recommended?
An MRI for sacrum scan is typically recommended when a healthcare provider suspects a condition affecting the sacrum, pelvic area, or lower spine. The scan helps diagnose issues with bones, nerves, muscles, and soft tissues that might not be visible with other imaging techniques like X-rays. Here are the most common scenarios when an MRI for the sacrum is recommended:
- Chronic Lower Back or Pelvic Pain
When it’s recommended: Persistent or unexplained pain in the lower back, pelvic region, or buttocks that does not improve with conservative treatments like rest, physical therapy, or medications.
- Suspected Spinal or Sacral Fractures
When it’s recommended: After a traumatic injury such as a fall, car accident, or sports-related accident, or if there is a suspicion of a stress fracture in the sacrum.
- Sciatica or Nerve Compression
When it’s recommended: If you experience symptoms like leg pain, numbness, tingling, or weakness in the legs, often as a result of sciatic nerve compression from issues like herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Suspected Tumors or Infections
When it’s recommended: If there are concerns about unexplained weight loss, fever, or localized pain that may indicate a tumor, infection, or abscess in the sacral area, such as osteomyelitis (bone infection) or spinal tumors.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome
When it’s recommended: If you experience severe lower back pain, loss of bladder or bowel control, numbness around the saddle area (groin, buttocks, or thighs), or weakness in the legs, which may indicate cauda equina syndrome, a serious compression of the nerve roots at the end of the spinal cord.
Benefits of MRI for Sacrum Scan
An MRI for the sacrum provides numerous advantages when diagnosing and evaluating conditions affecting the sacral region, lower spine, and pelvic area. With its non-invasive, detailed imaging capabilities, MRI is a valuable tool for both diagnosis and treatment planning. Here are the key benefits of an MRI for sacrum scan:
- Non-invasive and Safe
No Radiation: Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option, especially for patients who may require repeated scans or those who are sensitive to radiation exposure.
- Detailed Imaging of Soft Tissues
High-Resolution Images: MRI provides exceptional clarity and detail of soft tissues, including muscles, ligaments, nerves, and intervertebral discs. This is particularly useful for diagnosing conditions affecting the sacral nerves or the sacroiliac joints.
- Accurate Diagnosis of Bone and Joint Conditions
Bone and Joint Assessment: MRI provides detailed images of both bones and joints, making it highly effective for identifying conditions like sacroiliitis, spondylolisthesis, and spinal fractures. This detailed view allows for better understanding of the extent and location of damage or disease.
- Effective for Detecting Tumors and Infections
Identifying Abnormal Growths: MRI is highly sensitive to abnormal growths, including benign and malignant tumors, cysts, and metastases from cancers elsewhere in the body. Tumors in the sacral area or spine can be precisely located and assessed for their size and impact on surrounding tissues.
- Clear Visualization of Nerve Compression and Damage
Assessing Nerve Function: MRI allows for clear visualization of nerve roots in the sacral region, making it ideal for diagnosing conditions like sciatica, cauda equina syndrome, and other forms of nerve compression. These conditions can cause pain, numbness, or weakness in the legs and pelvic area.
- Assessment of Spinal Alignment and Integrity
Spinal Disorders: MRI is particularly useful for diagnosing issues such as spondylosis, herniated discs, or spinal stenosis in the sacral or lower lumbar spine. It helps in evaluating the alignment and integrity of the spine, which is essential for patients with chronic back pain or history of trauma.
Preparation for Your MRI for Sacrum Scan
Preparing for an MRI of the sacrum is relatively simple, but it’s important to follow a few guidelines to ensure the procedure goes smoothly and the results are as accurate as possible. Here’s what you can expect and how to prepare:
- Inform Your Doctor About Any Health Conditions
Medical History: Tell your doctor about any chronic health conditions, allergies, or current medications you’re taking. Some conditions, like kidney disease, may require special considerations, especially if a contrast agent (gadolinium) is being used.
- Remove Jewelry and Metal Objects
Before the Scan: Remove all jewelry, piercings, watches, hairpins, or any other metallic objects. Metal can interfere with the MRI’s magnetic field and distort the images, making it difficult to obtain clear results.
Clothing: You may be asked to change into a hospital gown to ensure no metal zippers, buttons, or fasteners are in the way during the scan.
- Avoid Eating or Drinking (If Required)
Fasting Instructions: In some cases, you may be instructed to fast (not eat or drink) for a few hours before the procedure. This is typically required if a contrast dye is being used, though it’s not always necessary for a sacrum scan.
- Arrive Early
Appointment Timing: Arrive at least 15-30 minutes before your scheduled MRI time. This will allow you time to complete any necessary paperwork, undergo any preliminary checks, and discuss your medical history with the radiology staff.
- Discuss Anxiety or Claustrophobia Concerns
Feeling Claustrophobic?: If you feel anxious or claustrophobic at the thought of being in the MRI machine, let the staff know ahead of time. They can provide calming measures, such as a sedative or an open MRI machine (if available), which might help reduce discomfort during the scan.
- Test Type: MRI Sacrum Scan
- Preparation:
- Wear a loose-fitting cloth
- You may need to fast for up to four hours before
- Carry Your ID Proof
- Prescription is mandatory for patients with a doctor’s sign, stamp, with DMC/HMC number; as per PC-PNDT Act
- Reports Time: With in 4-6 hours
- Test Price: Rs.4000
How can I book an appointment for a MRI For Sacrum Scan through Medintu?
To schedule an appointment for a MRI For Sacrum Scan, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is an MRI for Sacrum Scan?
An MRI for sacrum scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the sacrum, lower spine, and surrounding soft tissues (nerves, muscles, ligaments). It helps diagnose conditions like fractures, tumors, nerve compression, and inflammation in the sacral region.
Is an MRI for Sacrum Scan Safe?
Yes, MRI is generally very safe. It does not use ionizing radiation (unlike X-rays or CT scans) and is non-invasive. However, it is important to inform your doctor about any metal implants, pacemakers, or other devices in your body, as the magnetic field could interfere with these devices.
How Long Does an MRI for Sacrum Take?
The MRI scan typically takes between 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the complexity of the images needed and whether a contrast agent is used. During the scan, you will need to remain as still as possible to ensure clear images.
Do I Need to Prepare for an MRI of the Sacrum?
Yes, some preparation is required:
- Remove any metal objects (e.g., jewelry, piercings, watches) before the scan.
- Inform your doctor of any metal implants or medical conditions.
- Follow fasting instructions if contrast dye is used.
- Arrive early to allow time for paperwork and pre-scan assessments.
Will I Feel Anything During the MRI Scan?
No, the MRI scan is painless. However, the machine may make loud noises during the process, so you will be given earplugs or headphones to minimize the sound. Some people may feel slight discomfort from lying still for a period of time, but the scan itself is not painful.
Do I Need Contrast Dye for the MRI Sacrum Scan?
Not always. Contrast dye (gadolinium) is sometimes used to improve the quality of images, especially when assessing soft tissues, tumors, or inflammation. If contrast is needed, it will be injected through an IV in your arm. If you have concerns about the contrast, such as allergies, inform your doctor beforehand.
Can I Resume Normal Activities After the MRI?
Yes, you can generally resume your normal activities immediately after the MRI, unless you received a sedative before the procedure. If sedated, you may need someone to drive you home.
Why Choose Medintu for MRI Sacrum Scan?
Medintu is an online medical consultant that provides home-based medical services not only in your area but also in most cities in India, including Hyderabad, Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, and more. We have collaborated with diagnostic centers that have the best machines and equipment to ensure you get accurate results. Medintu provides 24-hour customer service for booking the appointment of the services and guides you with instructions. Medintu also provides the best diagnostic centers at low prices. Once you receive your test results, you can easily book an appointment with our network of experienced doctors for consultation. To schedule an appointment for a MRI For Sacrum Scan, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.