Fill out form to enquire now
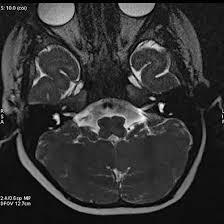
MRI Internal EAR
Medintu has collaborated with the best pathology laboratories that are NABL and NABH certified and follow ISO safety guidelines to provide the best MRI For Internal EAR at an affordable price for needy individuals. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a popular equipment that employs strong magnetic fields accompanied by Radiofrequency pulses to display clear images of the human organs. MRI is particularly helpful in imaging the internal ear where many conditions of the auditory and vestibular systems may originate from. The structures of internal ear or inner ear include cochlea, vestibule, and the three semicircular canals involved in hearing and balance respectively. MRI offers significant advantages in certain pathology, including tumours (acoustic neuromas), anomalies of the internal ear, and inflammation. MRI takes very clear images that can help to identify alterities at the level of inner ear structures. It often requires the patient to lie on their back on a cylindrical MRI machine from which a number of images are taken. There is always an option to use additional techniques, like contrast enhanced MRI in order to have even better visualization of certain lesions or abnormalities.
To schedule an appointment for an MRI For Internal EAR, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is an MRI?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a powerful diagnostic tool that provides detailed images of the body’s internal structures. Unlike X-rays or CT scans, MRI uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create high-resolution images without exposing patients to ionizing radiation. Here’s a closer look at how MRI works, its benefits, and its applications.
How MRI Works
1.Fields:
MRI machines contain powerful magnets that generate a strong magnetic field. This field aligns the hydrogen atoms in the body, which are abundant due to the high water content of tissues.
2.Radio Waves:
Once the hydrogen atoms are aligned, radio waves are emitted into the body. These waves temporarily disturb the alignment of the atoms.
3.Signal Detection:
When the radio waves are turned off, the hydrogen atoms return to their original alignment, releasing energy in the process. MRI sensors detect this energy, which is then converted into detailed images of the internal structures.
Benefits of MRI
- Non-Invasive: MRI is a non-invasive procedure, meaning it doesn’t require incisions or injections, making it safer for patients.
- No Ionizing Radiation: Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use harmful radiation, reducing the risk of long-term exposure.
- High-Resolution Imaging: MRI produces exceptionally clear images of soft tissues, making it invaluable for diagnosing conditions affecting organs, muscles, and joints.
- Multiplanar Imaging: MRI can produce images in multiple planes (axial, coronal, sagittal), providing comprehensive views of complex anatomical structures.
Common Applications of MRI
- Neurological Disorders: MRI is widely used to diagnose brain tumors, strokes, multiple sclerosis, and other neurological conditions.
- Musculoskeletal Imaging: It is effective in evaluating joint injuries, cartilage damage, and spinal disorders.
- Abdominal Imaging: MRI can assess liver diseases, pancreatic disorders, and other abdominal conditions.
- Cardiovascular Imaging: It helps visualize blood vessels and heart structures, providing insights into cardiovascular diseases.
Indications for MRI of the Internal Ear
MRI of the internal ear is a critical imaging tool used to evaluate various conditions affecting the ear and surrounding structures. Here are some common indications for performing an MRI of the internal ear:
- Hearing Loss
Persistent or sudden hearing loss that cannot be explained by routine examinations may warrant an MRI to identify potential underlying causes, such as tumors or structural abnormalities.
- Tinnitus
Patients experiencing persistent tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears) may undergo MRI to rule out conditions like acoustic neuromas or other lesions affecting the auditory pathways.
- Balance Disorders
Issues with balance, dizziness, or vertigo can indicate problems with the inner ear. MRI helps assess conditions like vestibular schwannomas or labyrinthitis.
- Acoustic Neuroma
This benign tumor, also known as vestibular schwannoma, develops on the nerve that connects the inner ear to the brain. MRI is crucial for diagnosing and monitoring this condition.
- Cholesteatoma
A cholesteatoma is an abnormal skin growth in the middle ear that can damage surrounding structures. MRI can help evaluate the extent of the growth and its impact on nearby tissues.
- Infections
Recurrent ear infections or complications from otitis media may necessitate MRI to assess for abscesses, inflammation, or other complications.
- Congenital Abnormalities
MRI is useful in identifying congenital malformations of the inner ear, helping to guide management and treatment options.
- Trauma
Following head or ear trauma, MRI can help identify internal ear injuries, fractures, or hematomas that may not be visible on other imaging modalities.
- Evaluation of Tumors
MRI can be used to evaluate primary tumors of the ear and surrounding structures, as well as metastatic lesions that may have spread to the area.
- Post-Surgical Evaluation
After ear surgery, MRI may be employed to assess for complications, such as residual tumors or changes in the anatomy of the ear.
The MRI Procedure
The MRI procedure is a non-invasive and relatively straightforward process that typically involves several key steps. Here’s what patients can expect during an MRI of the internal ear:
- Preparation for the MRI
Consultation: Before the scan, patients will have a consultation with their healthcare provider to discuss symptoms and medical history.
Instructions: Patients may receive specific instructions, such as fasting for a few hours if contrast will be used or avoiding certain medications.
Metal Screening: It’s crucial to inform the medical staff about any metal implants, pacemakers, or other devices, as these may interfere with the MRI machine.
- Arrival at the Imaging Center
Check-In: Upon arrival, patients will check in and may need to fill out a questionnaire regarding medical history and any potential contraindications.
Changing Clothes: Patients might be asked to change into a hospital gown and remove any metal objects, including jewelry, watches, and hairpins.
- The MRI Scan
Positioning: Patients will lie on a padded table, usually on their back. For an internal ear MRI, the position may vary depending on the area of interest.
Use of Contrast: If contrast is needed, it will be administered through an intravenous (IV) line before or during the scan. Patients should be monitored for any allergic reactions.
Entering the MRI Machine: The table will slide into the MRI machine, which is a large, cylindrical tube. Patients will be instructed to remain as still as possible throughout the scan to ensure clear images.
Communication: Patients will be given a call button to communicate with the technologist if needed. Additionally, they may receive earplugs or headphones to help minimize noise from the machine.
- During the Scan
Duration: The MRI scan typically lasts between 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the specific protocol and whether additional sequences are required.
Noise Levels: Patients can expect to hear loud thumping or tapping sounds during the scan, which is normal. The use of headphones or earplugs can help reduce discomfort from the noise.
Interpreting MRI Results
Interpreting MRI results is a critical step in diagnosing and managing conditions affecting the internal ear. Here’s an overview of the process and what to expect when reviewing MRI findings.
- Role of the Radiologist
Expert Analysis: MRI images are evaluated by a radiologist, a medical doctor specializing in imaging studies. They analyze the scans for abnormalities and prepare a detailed report.
Collaboration: The radiologist collaborates with the referring physician to discuss findings and implications for patient care.
- Key Aspects of MRI Interpretation
Anatomical Structures: Radiologists assess the images for the presence and condition of key structures in the internal ear, including the cochlea, vestibular apparatus, and auditory nerve.
Identification of Abnormalities: Common abnormalities evaluated include:
Tumors: Identification of benign or malignant growths, such as acoustic neuromas or other lesions.
Inflammation: Signs of conditions like labyrinthitis or chronic ear infections.
Cysts and Cholesteatomas: Presence and extent of cystic formations or abnormal skin growths.
Fluid Collections: Evaluation of any fluid accumulation that may indicate infection or other issues.
- Types of Findings
Normal Results: A report may indicate that the internal ear structures are normal and functioning as expected.
Abnormal Results: If abnormalities are detected, the report will describe them in detail, including size, location, and potential implications.
- Implications for Treatment
Diagnosis: The findings will help the healthcare provider diagnose the specific condition affecting the patient.
Treatment Planning: Based on the MRI results, treatment options may include:
Monitoring: In cases of small, benign tumors or mild conditions.
Medication: For infections or inflammatory conditions.
Surgery: If significant abnormalities, such as tumors or cholesteatomas, are found.
- Follow-Up and Next Steps
Discussion with Healthcare Provider: Patients should schedule a follow-up appointment to discuss the MRI results with their healthcare provider, who will explain the findings in detail and recommend further action.
Additional Testing: In some cases, further imaging studies or tests may be necessary to gather more information or clarify findings.
Advantages and Limitations
Advantages
1.Non-Invasive Procedure
MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique, meaning it doesn’t require surgery or incisions, reducing the risk associated with diagnostic procedures.
2.High-Resolution Imaging
MRI provides detailed images of soft tissues, allowing for precise visualization of structures within the internal ear, such as the cochlea and vestibular apparatus.
3.No Ionizing Radiation
Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI does not use ionizing radiation, making it a safer option for patients, especially for those requiring multiple imaging studies.
4.Multiplanar Imaging
MRI can produce images in various planes (axial, coronal, sagittal), providing comprehensive views of complex anatomical structures and helping in accurate diagnosis.
5.Enhanced Contrast
The use of gadolinium-based contrast agents improves the visibility of certain tissues and can help distinguish between normal and abnormal structures.
6.Functional Assessment
Advanced MRI techniques can evaluate blood flow and metabolic activity, providing insights into the functional status of ear structures.
Limitations
1.Cost and Accessibility
MRI can be more expensive than other imaging modalities, and availability may be limited in certain areas or facilities, affecting patient access.
2.Time-Consuming
The MRI scan can take longer than other imaging procedures, sometimes lasting up to an hour, which may be inconvenient for patients.
3.Patient Anxiety and Claustrophobia
Some patients may feel anxious or claustrophobic inside the MRI machine, which can impact their ability to remain still during the scan.
4.Metal Implants and Contraindications
Patients with certain metal implants, such as pacemakers or specific aneurysm clips, may not be suitable candidates for MRI due to the strong magnetic fields.
5.Motion Artifacts
Any movement during the scan can lead to blurred images, which can compromise the quality of the results.
6.Limited Information on Bone Structures
MRI is less effective for imaging bony structures compared to CT scans, so it may not be the best option for evaluating bone-related issues in the ear.
7.Interpretation Variability
The accuracy of MRI interpretation depends on the expertise of the radiologist. Misinterpretation can lead to incorrect diagnoses or treatment plans.
Advancements in MRI Technology
The field of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is continually evolving, with significant advancements that enhance imaging quality, patient comfort, and diagnostic capabilities. Here are some of the key advancements in MRI technology:
- Higher Magnetic Field Strengths
3.0 Tesla and Beyond: Modern MRI machines often operate at higher field strengths (3.0 Tesla and above), providing improved resolution and contrast, allowing for more detailed images of soft tissues in the internal ear.
- Faster Imaging Techniques
Parallel Imaging: This technology accelerates the scanning process by using multiple coils to capture data simultaneously, significantly reducing scan times.
Compressed Sensing: Advanced algorithms enable faster image acquisition without sacrificing quality, allowing for quicker patient throughput.
- Advanced Contrast Agents
New Gadolinium Formulations: Innovations in contrast agents enhance visualization of blood vessels and lesions, improving diagnostic accuracy while minimizing side effects.
- Functional MRI (fMRI)
Assessing Brain Activity: fMRI can be applied in neurology to evaluate brain activity and connectivity, which is particularly useful when considering conditions that may impact the inner ear’s role in balance and hearing.
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
Mapping Neural Pathways: DTI provides insights into the integrity of neural pathways, which can be valuable in assessing conditions that affect auditory processing.
- 3D Imaging Techniques
Comprehensive Visualization: Advances in 3D imaging allow for detailed views of the ear’s complex anatomy, aiding in surgical planning and diagnosis of conditions such as tumors or structural abnormalities.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Enhanced Image Analysis: AI algorithms can assist in image interpretation, identifying patterns and abnormalities more quickly and accurately, potentially reducing the risk of human error.
- Portable MRI Systems
Increased Accessibility: Developments in portable MRI technology enable imaging in emergency situations or remote locations, making MRI more accessible to patients who might not otherwise receive timely care.
- Patient Comfort Innovations
Wider Bore Designs: Newer MRI machines with wider openings reduce feelings of claustrophobia, making the experience more comfortable for patients.
Improved Noise Reduction: Enhanced acoustic designs and noise-canceling technology help reduce the loud noises associated with MRI scans, further improving patient comfort.
- Integration with Other Modalities
Hybrid Imaging Techniques: Combining MRI with other imaging modalities, such as PET/MRI, provides complementary information that can enhance diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
- Test Type: MRI For Internal EAR
- Preparation:
- Wear a loose-fitting cloth
- Fasting not required
- Carry Your ID Proof
- Prescription is mandatory for patients with a doctor’s sign, stamp, with DMC/HMC number; as per PC-PNDT Act
- Reports Time: With in 3-4 hours
- Test Price: Rs.4000
How can I book an appointment for an MRI For Internal EAR through Medintu?
To schedule an appointment for an MRI For Internal EAR, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is an MRI of the internal ear?
An MRI of the internal ear is a specialized imaging technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the ear’s structures, including the cochlea, vestibular apparatus, and auditory nerve.
Why is an MRI of the internal ear performed?
MRI is used to diagnose various conditions affecting the ear, such as tumors (e.g., acoustic neuromas), infections, congenital abnormalities, and causes of hearing loss or balance issues.
Is an MRI scan painful?
No, an MRI scan is non-invasive and generally painless. Patients may experience some discomfort from lying still or anxiety from the enclosed space, but the procedure itself does not cause pain.
How long does an MRI of the internal ear take?
The scan typically lasts between 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the specific protocols and whether contrast agents are used.
Do I need to prepare for the MRI?
Preparation may include fasting for a few hours before the procedure, especially if contrast will be administered. It’s important to follow any specific instructions given by your healthcare provider.
Will I need a contrast agent for my MRI?
In some cases, a gadolinium-based contrast agent may be used to enhance the images. Your healthcare provider will determine if this is necessary based on your condition.
What should I expect during the MRI?
You will lie on a padded table that slides into the MRI machine. You’ll need to remain still during the scan, and you may hear loud noises. Earplugs or headphones are usually provided to minimize discomfort.
Are there any risks associated with MRI?
MRI is considered safe for most patients. However, individuals with certain metal implants, pacemakers, or other contraindications may not be suitable candidates. Always inform your provider about any medical devices.
How are the MRI results interpreted?
A radiologist will analyze the images and provide a report detailing any findings. Your healthcare provider will discuss the results with you and recommend any necessary follow-up actions.
What happens after the MRI?
After the scan, you can typically resume normal activities. If contrast was used, you may be advised to drink plenty of fluids to help eliminate it from your system.
Why Choose Medintu for MRI Internal EAR?
Medintu is an online medical consultant that provides home-based medical services not only in your area but also in most cities in India, including Hyderabad, Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, and more. We have collaborated with diagnostic centers that have the best machines and equipment to ensure you get accurate results. Medintu provides 24-hour customer service for booking the appointment of the services and guides you with instructions. Medintu also provides the best diagnostic centers at low prices. Once you receive your test results, you can easily book an appointment with our network of experienced doctors for consultation. To schedule an appointment for an MRI For Internal EAR, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.