Fill out form to enquire now
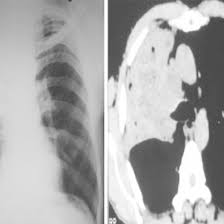
CECT For Guided FNAC
Medintu has collaborated with the best pathology laboratories that are NABL and NABH certified and follow ISO safety guidelines to provide the best CECT For Guided FNAC at an affordable price for needy individuals. Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography, or CECT for Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology, is a novel diagnostic technique that involves high-resolution imaging with the less invasive FNAC procedure. FNAC is the medical procedure of taking tissue samples from abnormal growths or masses, thus giving the doctor an idea of what the lesion is made up of—whether it’s benign or malignant. When it’s combined with CECT, this procedure becomes much more potent and provides high-resolution real-time images that will lead the physician to the lesion at its exact location to place the needle accurately and retrieve an optimal sample.
The use of CECT is particularly useful for guiding FNAC when dealing with deep-seated or hard-to-reach lesions, which may be located in the lungs, liver, or abdominal cavity. These sites are usually inaccessible by direct FNAC techniques, but CECT allows for pinpoint targeting of abnormal tissues or tumors that might otherwise have been missed or sampled incorrectly. The contrast agent, therefore, provides the improved imaging that ensures correct positioning of the needle while it reduces the risk of complications and improves the yield in diagnosis. To schedule an appointment for a CECT For Guided FNAC, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is CECT and FNAC?
- CECT and FNAC are both diagnostic procedures used in medical practice, but they serve different purposes:
- CECT (Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography)
1.Definition: CECT is CT scan where a contrast dye, usually iodine-based, is injected into the bloodstream, or taken orally to produce images of internal organs and tissue. This way, structures can be visualized more clearly within the body and abnormalities such as tumors, infections, and blood vessel issues can be discovered.
2.How it works: A CT scan uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the body, and the contrast material helps highlight areas of interest, making them stand out more clearly on the images.
3.Common uses: CECT is typically used for:
4.Identifying tumors or masses
5.Evaluating blood vessels (e.g., aneurysms, blockages)
6.Assessing organs like the brain, liver, lungs, and kidneys
7.Detecting infections or inflammatory conditions
8.Advantages: It provides detailed 3D imaging and is non-invasive.
2.FNAC-Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology
- 1.Definition: FNAC is a diagnosis method in which a thin hollow needle is used to aspirate tissue or cells from a suspect mass or lesion. A specimen is obtained by this fine needle aspiration cytology and then sent to the laboratory for study. The sample is inspected through a microscope to verify if it is benign or malignant to provide a differential diagnosis.
- 2.How it works: A needle is inserted into the area of concern, such as a lump in the breast, thyroid, or lymph nodes, and cells extracted are sent to a laboratory for cytological analysis.
- 3.Common uses: FNAC is generally used for:
- 4.Cancer diagnosis or benign tumors
- 5.Examining lumps or masses in various parts of the body, such as breast, lymph nodes, thyroid, and liver
- 6.Detecting infections or inflammatory diseases in specific tissues
- 7.Advantages: FNAC is minimally invasive, can be performed on outpatients, and the results are quickly seen.
How CECT Guides FNAC?
CECT (Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography) can play a crucial role in guiding FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology), especially when the lesion or abnormality being investigated is difficult to locate or access with the naked eye or physical examination alone. Here’s how CECT guides FNAC:
- Improved Localization of Lesions
- CECT provides detailed images of the internal anatomy, which helps doctors precisely locate the lesion or mass, even if it’s deep within the body or in an area that’s hard to reach. This is particularly helpful when the abnormality is in organs like the liver, lungs, kidneys, or deep lymph nodes.
- Contrast material makes the boundaries of the abnormal area more visible, thereby enabling better assessment of the lesion size, shape, and even exact location.
- Characteristic Assessment of the Lesion
- CECT may help determine whether the lesion is solid or cystic, its vascularity (whether it contains blood vessels), and whether it has a relationship with surrounding structures.
- This information will guide the placement of the needle during FNAC so that the biopsy is obtained from the most relevant or representative part of the lesion, reducing the chances of an unrepresentative sample.
- Real-Time Guidance During FNAC
- CT-guided FNAC: In some cases, one can use real-time CECT to guide the FNAC. The CT scanner allows continuous imaging during the biopsy, in which the doctor can see exactly where the needle is in relation to the lesion before inserting it.
- The position of the needle can then be adjusted by the radiologist or interventional physician by using live CECT images such that it precisely hits the lesion even in very difficult locations.
- Minimization of Risk
- For lesions adjacent to critical structures such as blood vessels, nerves, or vital organs, CECT enables the physician to outline the anatomy of these areas and to avoid causing damage to these areas during FNAC.
- CECT avoids unnecessary trauma to the surrounding tissues by offering clear visualization of where to place the needle and how to advance it safely.
- Assisting Biopsy in Difficult Areas
- For lesions that lie deep or for inaccessible areas (such as in the lung, retroperitoneum, or mediastinum), CECT will be beneficial since it directs FNAC at very high spatial resolution reducing the need to resort further for more-invasive surgeries.
- CECT will benefit the case by targeting the right clinically significant site in lesions of multiple entities.
- Pre-FNAC Planning
- CECT gives an overview of the lesion’s relation to the surrounding structures, thus facilitating pre-procedure planning. The doctor can thus ascertain the best approach to access the lesion for biopsy, including the optimal angle and pathway for the insertion of the needle.
Benefits of CECT for Guided FNAC
CECT (Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography) provides significant advantages for guiding FNAC (Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology) in challenging and complex cases where accurate biopsy is the key. These are key benefits listed below:
- Increased precision in lesion targeting
- Accurate Localization: CECT offers high-resolution, cross-sectional images that allow for the accurate localization of lesions, even those that are deep, small, or hard to reach. This ensures that the needle is directed precisely to the site of interest.
- Clear Delineation: The contrast material enhances the visibility of the lesion by highlighting the abnormal tissue against the surrounding structures, making it easier to identify and avoid normal tissue or critical structures.
- Improved Safety
- Minimized Risk of Injury: The use of CECT provides guidance to minimize the chances of injury to the surrounding structures. For instance, if a lesion is adjacent to vital organs or blood vessels, such as in the case of liver, lung, or kidney lesions, CECT will help guide the needle to avoid these structures and thus prevent complications such as bleeding or organ damage.
- Real-Time Monitoring: The process of CT-guided FNAC allows for using CECT for real-time monitoring of the needle as it passes. This makes it impossible for the procedure to get misplaced, mainly in more complicated anatomical regions.
- Assessment of Lesion Characteristics
- Delineation of Type of Lesion: Through CECT, detailed composition of the lesion, its vascularity, and even the involvement of surrounding structures can be seen. Such characteristics may assist in determining which method for FNAC would most likely retrieve an accurate sample.
- Multi-phase Imaging: Sometimes, CECT includes imaging at different phases (such as arterial, venous phases), thereby better characterizing the lesion and ensuring that the FNAC targets the most relevant portion of the mass.
- Improved Visualization of Deep or Inaccessible Lesions
- Accessing Deep Lesions: CECT can guide more safely lesions placed in areas that are hard to access or visualize, such as the lungs, retroperitoneum, or mediastinum, because enhanced images provide clear mapping of deep-seated masses that may otherwise be missed.
- Guiding Biopsy of Small Lesions: Small, sub-centimeter lesions that are difficult to palpate or see on ultrasound can be better visualized with CECT, improving the chances of obtaining a representative sample.
- Real-Time Image Guidance for Precision
- Live Imaging: With CT-guided FNAC, the physician continuously observes the placement of the needle through CECT imaging. This enables real-time adjustment of the needle to avoid deviation and reach the lesion directly, which is quite useful for lesions close to other organs or tissues.
- Lessened Procedure Time: An accurate guidance often allows completion of the biopsy procedure sooner. This minimizes discomfort for the patient and also limits exposure to radiation.
- Reduced Need for Surgical Intervention
- Non-invasive Sampling: The process of CECT-guided FNAC is non-invasive compared to a surgical biopsy. Preciseness of CECT brings reduced dependency on more aggressive, surgically invasive intervention processes when lesions are harder to access or diagnose through it.
- Effective for Inoperable Lesions: CECT-guided FNAC can be used for lesions that are not amenable to surgical excision, such as those located in critical areas or those in patients who are poor surgical candidates.
When is CECT-Guided FNAC Recommended?
Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography-guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology is recommended for certain scenarios where conventional FNAC or other imaging modalities cannot be used. The important clinical scenarios where CECT-guided FNAC proves particularly useful are as follows:
- Deep-Seated Lesions
- Suggestion: CECT-guided FNAC is best used for lesions located deep within the body and cannot be accessed via palpation or even visualized by surface imaging, such as ultrasound.
- Reason: CECT provides clear imaging of deep structures and helps the clinician navigate safely to obtain a sample without injuring surrounding tissues.
- Small or Inaccessible Lesions
- Recommendation: CECT-guided FNAC is recommended for small lesions (e.g., sub-centimeter masses) or those in anatomically difficult-to-reach areas where the lesion may be missed on conventional FNAC or ultrasound.
- Reason: CECT enhances visualization, making it easier to pinpoint small, hard-to-reach lesions.
- Lesions Near Critical Structures
- Recommendation: CECT-guided FNAC is recommended when the lesion is near or involves critical structures such as blood vessels, nerves, or vital organs.
- Reason: The enhanced imaging from CECT helps navigate the needle away from vital structures, minimizing risk and avoiding complications.
- Tumors with Invasive or Metastatic Features
- Recommendation: CECT-guided FNAC is useful in tumors with suspected invasive growth or metastatic disease where tissue sampling representative of the neoplasm is important in diagnosis and staging.
- Reason: CECT aids to differentiate primary from metastatic lesions and to pinpoint the location for accurate sampling.
- Lesions Not Easily Identified with Ultrasound or CT End
- Recommendation: CECT is used to enhance the visibility of the lesion in case it is not well visualized by conventional imaging and provides a guide for FNAC.
- Reason: The contrast agent in CECT enhances tissue differentiation, making it easy to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions and navigate the needle to the correct location.
- Multi-Lesion Cases
- Recommendation: CECT-guided FNAC is recommended in patients with multiple lesions where precise targeting is required to sample the most clinically significant lesion.
- Reason: CECT allows the clinician to identify and prioritize lesions for biopsy based on size, location, and suspected pathology, ensuring the most relevant tissue is sampled.
- Test Type: CECT For Guided FNAC
- Preparation:
- Wear a loose-fitting cloth
- Fasting not required
- Carry Your ID Proof
- Prescription is mandatory for patients with a doctor’s sign, stamp, with DMC/HMC number; as per PC-PNDT Act
- Reports Time: With in 4-6 hours
- Test Price: Rs.3000
How can I book an appointment for a CECT For Guided FNAC through Medintu?
To schedule an appointment for a CECT For Guided FNAC, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.
What is CECT, and how is it used in FNAC?
CECT stands for Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography. It is a type of CT scan, using contrast agents to better visualize the tissues and organs. In FNAC, CECT is used as a guide for the precise placement of the needle in collecting tissue samples from deep or hard-to-reach lesions. The contrast helps to highlight the abnormal areas, making it easier for the doctor to target the correct site during the procedure.
FNAC stands for Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology. It is a type of diagnostic procedure where tissue samples are drawn from a suspicious mass or lesion using a thin, hollow needle. It is mainly used in the diagnosis of conditions such as cancer, infections, or benign tumors. You may need FNAC if you have an abnormal lump, swollen lymph node, or other unexplained symptoms that require further evaluation to determine the cause.
How does CECT assist in guiding FNAC?
CECT shows the lesion or mass clearly and in detail, so that its accurate position, size, and relation to structures such as blood vessels or organs is visible. The use of contrast dye in CECT makes these tissues much more vivid, so that a physician can ensure that the needle is placed accurately within the target area to yield enough tissue for analysis.
Is the CECT-guided FNAC procedure painful?
The procedure itself is usually not painful, but you might experience some discomfort at the time of the insertion of the needle. The region being biopsied would be usually numbed by a local anesthetic to minimize the pain. Patients may feel some soreness or bruising at the site after the procedure; these symptoms resolve in most cases within a few days.
Is there any risk associated with CECT-guided FNAC?
While CECT-guided FNAC is safe in most cases, potential risks include:
- Bleeding: There might be some bleeding at the biopsy site.
- Infection: It has a small chance of infection where the needle enters the skin.
- Injury to the adjacent tissues: Though rarely reported, there is always the chance of accidentally hitting and injuring nearby structures such as blood vessels or organs.
- The patient might develop an allergic reaction to the contrast dye, though it is rare. The doctor will assess your risk factors and make the necessary preparations before performing the procedure on you.
How long does the CECT-guided FNAC procedure take?
This would take approximately 20 to 30 minutes. These are the time taken by the procedure to perform CECT scanning, insert the needle and obtain tissue sample. It can vary, but the FNAC part usually takes a very short time, sometimes less than five minutes.
What to expect after the procedure?
After the procedure, you may experience some minor discomfort or bruising at the site where the needle was inserted. Most patients are able to go home the same day, although you might be asked to stay for a short time for observation. You should avoid heavy physical activity for 24 to 48 hours after the procedure. Your doctor will give you specific aftercare instructions based on your individual case.
How soon will I get my FNAC results?
The tissue sample obtained during FNAC is sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results are usually available within 2–5 days. Your healthcare provider will contact you with the results and discuss the next steps, depending on the findings.
Why Choose Medintu for CECT For Guided FNAC?
Medintu is an online medical consultant that provides home-based medical services not only in your area but also in most cities in India, including Hyderabad, Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, and more. We have collaborated with diagnostic centers that have the best machines and equipment to ensure you get accurate results. Medintu provides 24-hour customer service for booking the appointment of the services and guides you with instructions. Medintu also provides the best diagnostic centers at low prices. Once you receive your test results, you can easily book an appointment with our network of experienced doctors for consultation. To schedule an appointment for a CECT For Guided FNAC, simply contact Medintu or call our customer care at +919100907036 or +919100907622 for more details and queries.